A Credit Score is a numerical representation of individual creditworthiness. This score is calculated by credit bureaus, such as Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion based on an individual's credit history. A Credit Score ranges from 300 to 850, with a higher score indicating better creditworthiness. Having a good credit score is essential for obtaining credit, such as loans or credit cards, with favorable terms and interest rates. A poor credit score can make it challenging to get approved for credit and may result in higher interest rates, making it more difficult to pay off debts. Credit Scores are important because they could impact an individual's ability to obtain credit such as loans or a credit card, and could affect the interest rate and terms of those loans. Therefore, it is important to understand the basics of credit scores and how to improve them:-
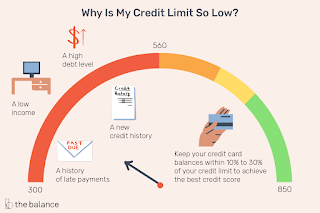
1. Payment History- Payment history is the most significant factor in calculating a credit score, accounting for 35% of the total score. It refers to an individual's history of making payments on credit accounts, including loans, credit cards, and other lines of credit. Late or missed payments can have a significant negative impact on a credit score, as they indicate a higher risk of defaulting on debts. Even a single missed payment can lower a credit score and remain on a credit report for up to seven years. On the other hand, making on-time payments can improve a credit score and demonstrate a borrower's creditworthiness to lenders. Consistently paying bills on time shows that an individual is responsible and reliable when it comes to managing their finances.
It's important to note that payment history doesn't just refer to credit accounts. Other bills, such as rent, utilities, and cell phone bills, may also be reported to credit bureaus and can affect a credit score if payments are missed or made late. Late payments can also result in penalty fees, increased interest rates, and other consequences, which can further harm an individual's finances. Therefore, it's crucial to make payments on time, every time, to maintain good credit and avoid additional fees and penalties.
2. Credit Utilization- Credit utilization is the amount of available credit an individual uses in relation to their credit limit. It is a significant factor in calculating a credit score, accounting for 30% of the total score. Maintaining a low credit utilization rate is crucial to achieving a good credit score and demonstrating creditworthiness to lenders. A high credit utilization rate can indicate that an individual is relying too heavily on credit and may be at risk of defaulting on debts. On the other hand, a low credit utilization rate shows that an individual is using credit responsibly and can handle additional credit if needed. To calculate credit utilization, divide the total amount of credit used by the total credit limit. For example, if an individual has a credit card with a $5,000 limit and has used $2,500 of that credit, their credit utilization rate is 50%. Keeping credit utilization below 30% is generally recommended to maintain a good credit score. For example, if an individual has a $10,000 credit limit, they should aim to use no more than $3,000 of that credit. Lowering credit utilization can be achieved by paying down balances or increasing credit limits. However, increasing credit limits can be a double-edged sword as it may lead to overspending and higher debt if not used responsibly. It's important to note that credit utilization is calculated on a per-account and overall credit utilization basis. Therefore, it's essential to monitor credit utilization across all credit accounts and aim to keep it low across the board.  |
We could calculate our credit score like this !!!
|
3. Length of Credit History- The length of an individual's credit history is another significant factor that affects their credit score. It measures the age of the individual's oldest credit account, as well as the average age of all their credit accounts. Generally, a longer credit history can demonstrate responsible credit usage and lead to a higher credit score. The length of credit history is crucial because it shows how long an individual has been managing credit responsibly. A long credit history can indicate that the individual is experienced in managing their finances and is less likely to default on debts. On the other hand, a short credit history may indicate that the individual is new to credit and has yet to establish a history of responsible credit usage. Lenders typically prefer to see a long credit history, as it shows that the individual has a track record of making on-time payments and managing credit responsibly. However, a short credit history doesn't necessarily mean that an individual will be denied credit.
Lenders may consider other factors, such as employment history and income when evaluating creditworthiness. To improve the length of credit history, individuals should keep their oldest credit accounts open and active, even if they are not using them regularly. Closing old credit accounts can shorten credit history and negatively impact a credit score. Therefore, it's generally recommended to keep old credit accounts open and use them responsibly. It's important to note that the length of credit history only accounts for 15% of the total credit score, so it's not as significant as payment history or credit utilization. However, long credit history can still positively impact a credit score and demonstrate creditworthiness to lenders.
4.
Credit Mix-
Credit mix is another factor that affects an individual's credit score. It refers to the types of credit accounts an individual has, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages. Having a mix of credit accounts can demonstrate that an individual can handle different types of credit responsibly, leading to a higher credit score. Having a diverse credit mix can indicate that an individual can handle different types of credit responsibly. For example, if an individual has both credit cards and installment loans, it shows that they can handle revolving credit and installment credit, respectively. Having a mix of credit accounts can demonstrate financial responsibility and lead to a higher credit score.
It's important to note that credit mix only accounts for 10% of the total credit score, so it's not as significant as payment history or credit utilization. However, having a diverse credit mix can still positively impact a credit score and demonstrate creditworthiness to lenders. To improve their credit mix, individuals should consider adding different types of credit accounts to their credit profiles. For example, if an individual only has credit cards, they may consider applying for an installment loan or a mortgage to diversify their credit mix. However, it's important to note that adding new credit accounts should be done responsibly and not lead to overspending or high levels of debt. It's recommended to start with small credit accounts and make payments on time to build a positive credit history and improve the credit mix gradually.
5. Limit new Credit Inquiries- Limiting new credit inquiries is another important factor that affects an individual's credit score. Every time an individual applies for new credit, it generates a hard inquiry on their credit report, which can negatively impact their credit score. A hard inquiry is a record that shows a lender or creditor has reviewed an individual's credit report as part of a credit application. Hard inquiries can stay on an individual's credit report for up to two years and can lower their credit score by a few points each time.
Therefore, it's essential to limit the number of new credit inquiries to avoid a negative impact on the credit score. Applying for multiple credit accounts within a short period can raise red flags to lenders and indicate that an individual is in financial distress or attempting to take on more debt than they can handle. To limit new credit inquiries, individuals should only apply for credit when necessary and avoid making multiple applications within a short period. When shopping for credit, such as a mortgage or car loan, individuals should aim to complete their applications within a short period to minimize the number of hard inquiries generated on their credit report. It's also essential to check for errors on the credit report regularly. If an individual notices any unauthorized hard inquiries, they should dispute them with the credit reporting agencies to have them removed from their credit report.
6. Public Records- Public records are another factor that can affect an individual's credit score. Public records include information such as bankruptcies, tax liens, and civil judgments, which can negatively impact a credit score. Bankruptcies occur when an individual is unable to pay off their debts and files for bankruptcy with the court. Bankruptcy can stay on an individual's credit report for up to ten years and can have a significant negative impact on their credit score. Tax liens occur when an individual fails to pay their taxes, and the government places a lien on their assets to secure payment. Civil judgments occur when an individual fails to pay a debt, and the creditor takes legal action to recover the debt. Public records are considered the most severe form of negative credit information and can cause significant damage to an individual's credit score.
Lenders and creditors view public records as a sign of financial instability and may be hesitant to approve credit applications or may offer less favorable terms and interest rates. To minimize the impact of public records on a credit score, it's essential to take steps to address the underlying financial issues that led to the public record. For example, if an individual has a tax lien, they should work with the government to set up a payment plan or pay off the debt in full. If an individual has bankruptcy on their credit report, they should work on rebuilding their credit by making timely payments on their remaining debts. It's also important to note that public records can stay on an individual's credit report for a long time, so it's crucial to take steps to address the underlying issues and improve credit behavior to minimize the impact on creditworthiness.
7. Collections- Collections are another factor that can negatively impact an individual's credit score. When an individual fails to make payments on a debt, the creditor may turn the account over to a collections agency to recover the debt. The collections agency will then try to collect the debt from the individual. Collections can stay on an individual's credit report for up to seven years from the date of the original delinquency. The presence of a collection account on a credit report can lower an individual's credit score by a significant amount, depending on the severity of the collection. To minimize the impact of collections on a credit score, it's essential to take steps to address the debt and work with the collections agency to come up with a payment plan. In some cases, it may be possible to negotiate a settlement for less than the full amount owed. It's also important to note that paying off a collection account will not remove it from an individual's credit report.
The collection account will remain on the credit report for up to seven years from the date of the original delinquency. To avoid collections, it's essential to make payments on time and communicate with creditors if there are financial difficulties that make it difficult to make payments. If an individual is struggling to make payments on multiple debts, they may want to consider credit counseling or debt consolidation to help them get back on track.  |
| Pay your credit card collection wisely !!! |
8. Credit Age- Credit age, also known as length of credit history, is another important factor that can affect an individual's credit score. Credit age refers to how long an individual has been using credit and the age of their oldest credit account. Credit age is an important factor because it demonstrates an individual's ability to manage credit over time. A longer credit history can indicate that an individual has a track record of responsible credit behavior, while a shorter credit history may make it more difficult for lenders to assess an individual's creditworthiness. To build credit age, it's essential to start using credit responsibly as early as possible. This can be done by opening a credit card or loan account and making timely payments on a regular basis. It's important to keep credit accounts open even if they are not being actively used, as closing an account can shorten the length of credit history.It's also important to note that credit age is only one factor that lenders consider when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. Lenders also consider other factors, such as payment history, credit utilization, and types of credit accounts. In general, a longer credit history can have a positive impact on an individual's credit score, as long as the credit accounts are being managed responsibly. However, it's important to remember that credit age is just one factor among many that lenders consider, and it's essential to focus on building a positive credit history overall.
9. Total Debt- Total debt is another important factor that can impact an individual's credit score. Total debt refers to the amount of debt an individual owes, including credit card balances, loans, and other types of debt. High levels of debt can negatively impact an individual's credit score by increasing their credit utilization, which is the amount of credit being used compared to the total credit available. High credit utilization can signal to lenders that an individual may be at risk of defaulting on their debts. To manage total debt, it's important to create a budget and prioritize paying down debts with the highest interest rates first. It's also important to avoid taking on new debts, such as opening new credit cards or taking out new loans, until existing debts are under control. In some cases, it may be beneficial to consider debt consolidation, which involves combining multiple debts into one loan with a lower interest rate. Debt consolidation can help make payments more manageable and reduce the overall amount of interest paid. It's important to note that while total debt can impact an individual's credit score, having some level of debt is not necessarily a bad thing. Lenders like to see that an individual has a mix of credit accounts, including loans and credit cards, and is able to manage debt responsibly.  |
Manage your debt properly !!!
|
Improving a credit score could take time, but there are several tips that individuals could follow to improve their credit score over time. Here are some tips for improving a credit score.
1. Pay Bills on time- Paying bills on time is one of the most important things individuals can do to improve their credit score. Payment history makes up 35% of an individual's FICO credit score and is one of the biggest factors lenders consider when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. Late or missed payments can significantly impact an individual's credit score and stay on their credit report for up to seven years. Late payments can signal to lenders that an individual may be a risky borrower and may result in higher interest rates or even a denial of credit in the future. To avoid late or missed payments, individuals can set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure bills are paid on time. Many credit card companies and lenders also offer online payment options that make it easy to stay on top of payments. If an individual is unable to make a payment on time, it's important to contact the lender or creditor as soon as possible to discuss alternative payment arrangements. Some lenders may be willing to work with individuals to set up a payment plan or defer payments to avoid late fees and negative impacts on credit scores.
 |
Pay your bills on time !!!
|
2. Keep Credit Utilization Low- Credit utilization is the amount of credit being used compared to the total credit available. For example, if an individual has a credit card with a $5,000 limit and a balance of $1,000, their credit utilization would be 20%. Keeping credit utilization low is important for maintaining a positive credit score. Credit utilization makes up 30% of an individual's FICO credit score and is one of the factors lenders consider when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. Ideally, individuals should aim to keep their credit utilization below 30%. High credit utilization can signal to lenders that an individual may be overextended financially and may not be able to handle additional credit. This can result in a lower credit score and may make it more difficult to obtain credit in the future. There are several strategies individuals can use to keep their credit utilization low. One strategy is to pay off credit card balances in full each month. This can help avoid interest charges and keep credit utilization low. Another strategy is to spread out purchases across multiple credit cards, rather than maxing out a single credit card. This can help keep credit utilization low and demonstrate responsible credit behavior to lenders. Individuals can also request a credit limit increase from their credit card issuer. This can increase the total credit available and lower credit utilization. However, it's important to be mindful of spending and not to increase spending habits after receiving a credit limit increase.

3. Limit New Credit Inquiries- Limiting new credit inquiries is an important factor in maintaining a positive credit score. New credit inquiries make up 10% of an individual's FICO credit score and are taken into consideration when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. Applying for new credit can result in a hard inquiry on an individual's credit report, which can lower their credit score. Hard inquiries stay on credit reports for up to two years and can impact credit scores for up to 12 months. To limit new credit inquiries, individuals should be mindful of the number of credit applications they submit. It's important to only apply for credit when necessary and to only submit applications for credit that are likely to be approved. Individuals should also be aware of the potential impact of multiple inquiries on their credit scores. If an individual is shopping around for credit, such as a mortgage or auto loan, it's important to do so within a short period of time. FICO allows a 45-day period for rate shopping, during which multiple inquiries for the same type of credit will be counted as a single inquiry. In addition, individuals should be cautious of unsolicited offers for credit, such as pre-approved credit card offers. While these offers may be tempting, submitting an application can result in a hard inquiry and potentially lower credit scores.

4. Maintain a mix of credit accounts- Maintaining a mix of credit accounts is another important factor in maintaining a positive credit score. Credit mix accounts for 10% of an individual's FICO credit score and is taken into consideration when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. A mix of credit accounts refers to having a combination of different types of credit accounts, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages. Having a mix of credit accounts can demonstrate to lenders that an individual can handle different types of credit responsibly. However, it's important to note that opening new credit accounts solely for the purpose of diversifying the credit mix may not have a significant impact on credit scores. Opening new credit accounts can result in hard inquiries and may lower credit scores temporarily. Instead, individuals should focus on responsibly managing the types of credit accounts they already have. For example, making on-time payments on credit cards and installment loans can demonstrate responsible credit behavior to lenders. Individuals should also be cautious of taking on too much debt in an effort to maintain a mix of credit accounts. Taking on too much debt can negatively impact credit scores and may make it more difficult to obtain credit in the future.
 |
| Not take much debt |
5. Keep Old Credit Account Open- Keeping old credit accounts open is an important factor in maintaining a positive credit score. The length of credit history accounts for 15% of an individual's FICO credit score and is taken into consideration when evaluating an individual's creditworthiness. Older credit accounts can demonstrate a longer credit history, which can be viewed positively by lenders. In addition, keeping old credit accounts open can also increase an individual's overall available credit, which can help keep credit utilization low. However, it's important to note that simply keeping old credit accounts open may not be enough to maintain a positive credit score. Individuals should also focus on responsibly managing those accounts, such as making on-time payments and keeping balances low. If an individual does choose to close an old credit account, it's important to be aware of the potential impact on their credit score. Closing a credit account can impact credit utilization and decrease the overall length of credit history. In addition, individuals should be cautious of closing credit accounts with a balance, as this can negatively impact credit utilization and credit scores.
 |
| Keep Old Credit Account open |
6. Monitor Credit Reports- Monitoring credit reports is an important aspect of maintaining a positive credit score. Credit reports contain information about an individual's credit history, including credit accounts, payment history, and credit inquiries. Monitoring credit reports can help individuals identify errors or inaccuracies that may be negatively impacting their credit scores. Credit reports can be obtained for free once a year from each of the three major credit reporting agencies: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. It's recommended that individuals obtain their credit reports from each agency at least once a year and review them for any errors or inaccuracies. If an error is identified, individuals should contact the credit reporting agency to dispute the error. The credit reporting agency is required by law to investigate the dispute and provide a response within a reasonable amount of time. In addition to reviewing credit reports for errors, individuals should also monitor their credit reports for signs of identity theft or fraudulent activity.
For example, if there are credit accounts on the report that the individual did not open, it may be a sign that their identity has been stolen. There are also several credit monitoring services available that can help individuals monitor their credit reports and alert them to any changes or potential fraud. Some credit monitoring services may also provide additional features, such as credit score tracking and identity theft protection.
 |
| Monitor your credit reports |
Improving a credit score can take time and effort, but by following these tips and consistently demonstrating responsible credit behavior, individuals can work towards improving their credit score over time.
















Comments
Post a Comment